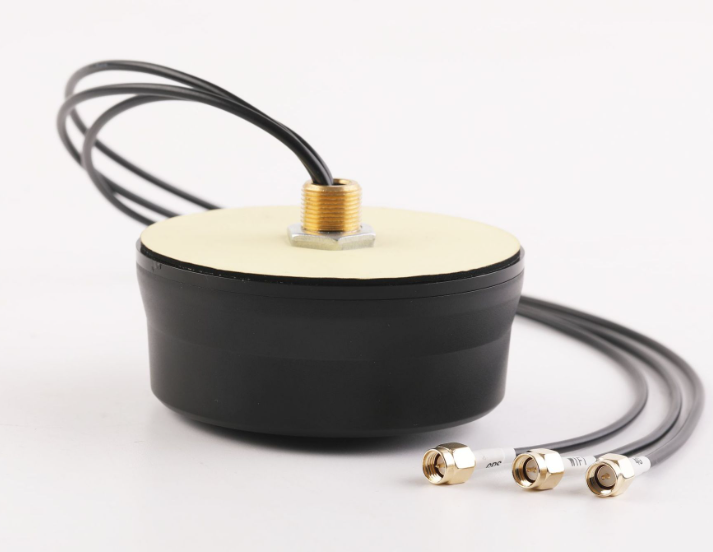
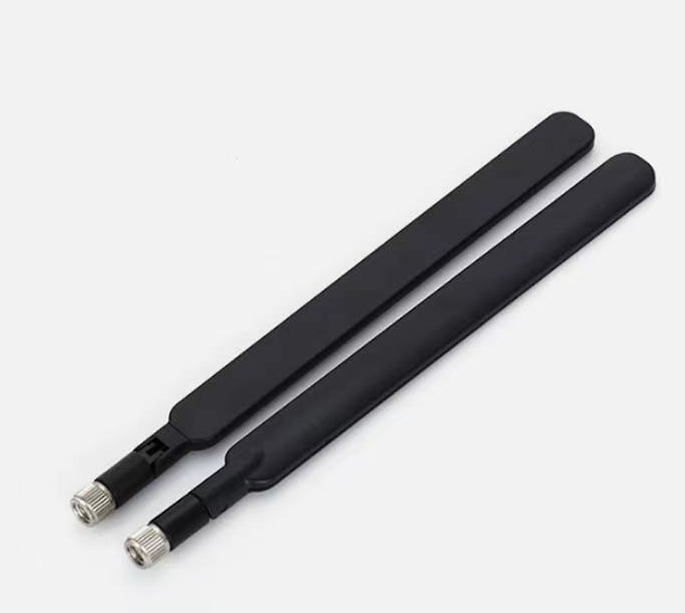
Gps Antenna shape
With the rapid development of Global Positioning system (GPS) technology, the shape design of GPS antenna, as a key component of receiving GPS signals, has been paid more and more attention. The shape of GPS antenna not only affects its receiving performance, but also determines the appearance and integration of the whole system. This paper will discuss the shape of GPS antenna and its importance in practical application.

The basic shape of GPS antenna
1. Spiral shape: spiral GPS antenna is one of the most common types. This design is famous for its excellent omni-directional performance and resistance to multipath effect. Because of its simple structure, easy to manufacture and low cost, it is widely used in all kinds of GPS equipment.
2. Plate shape: plate-shaped GPS antennas have wide bandwidth and stable gain, so they are suitable for applications requiring high precision. They are usually used in situations where high sensitivity reception is needed, such as navigation, aviation and land navigation.
3. Circularly polarized antenna: circularly polarized GPS antenna has excellent circularly polarized characteristics. It can receive signals from any direction and is not affected by antenna directionality. This kind of antenna is suitable for dynamic environment, such as mobile vehicles or ships.
4. Microstrip patch antenna: microstrip patch antenna is a small, lightweight GPS antenna, which has a wide application prospect. It has various shapes, including rectangle, circle, ring, etc., and is suitable for all kinds of equipment with limited space.
Effect of GPS Antenna shape on performance
The shape of the GPS antenna has a significant impact on its performance, and different shapes will affect the gain, directivity, polarization mode and impedance matching of the antenna. Because of its omni-directional receiving performance, the spiral antenna can show good performance in the environment with serious multipath effect, while the planar antenna is suitable for applications requiring high precision positioning because of its stable gain and high sensitivity.
Application example of GPS Antenna shape
1. Nautical applications: in the field of navigation, GPS antennas are usually installed on the top of ships to receive signals from GPS satellites. As ships move in the ocean, their antennas need to have good circularly polarized characteristics to adapt to the dynamic changes of ships. Circularly polarized GPS antennas are widely used in this kind of applications.
2. Aeronautical applications: in the aviation field, plate-shaped GPS antennas are more common. The high sensitivity and stable gain of this antenna enable it to provide accurate positioning information when flying at high speed. Some advanced aircraft also use microstrip patch antennas to achieve high-performance GPS reception in limited airborne space.
3. Land navigation: in land navigation applications, spiral GPS antennas are favored for their omni-directional reception performance and ability to resist multipath effects. this kind of antenna is usually installed on vehicles, mobile phones or other mobile devices to provide accurate positioning services.
4. Internet of things and smart devices: with the rapid development of the Internet of things and smart devices, microstrip patch antennas have been widely used in these devices because of their miniaturization and lightweight characteristics. These devices usually need to integrate high-performance GPS functions, and microstrip patch antennas are an ideal choice to achieve this goal.
The shape of GPS antenna has a decisive impact on its performance. Choosing the appropriate GPS antenna shape is very important to achieve high-performance GPS reception. In practical applications, we need to choose the appropriate GPS antenna shape according to specific application scenarios and requirements. With the rapid development of the Internet of things, smart devices and self-driving fields, the shape design of GPS antenna will face more challenges and opportunities. We look forward to further research and innovation to achieve GPS antenna shape diversification and performance optimization to meet the growing positioning needs.